
Benchmarking Model-robust Subsampling Functions
Source:vignettes/Benchmark_model_robust.Rmd
Benchmark_model_robust.Rmd## Error in get(paste0(generic, ".", class), envir = get_method_env()) :
## object 'type_sum.accel' not found
library(ggpubr)
library(tidyr)
library(dplyr)
# Theme for plots
Theme_special<-function(){
theme(legend.key.width=unit(1,"cm"),
axis.text.x = element_text(color = "black",size=14),
axis.text.y = element_text(color = "black",size=14),
strip.text = element_text(colour = "black",size = 16,face="bold"),
panel.grid.minor.x = element_blank(),
axis.title= element_text(color = "black",face = "bold",size = 14),
legend.text = element_text(color = "black", size=16),
legend.position = "bottom",
legend.margin=margin(0,0,0,0),
legend.box.margin=margin(-1,-2,-1,-2))
}
invisible(load("additionaldata/Results_Model_Robust.Rdata")) Setup
The lm(), biglm(), glm(), and
bigglm() functions are benchmarked against the model-robust
subsampling functions. This benchmarking is conducted across all three
regression problems using a consistent setup throughout. For large data
sizes \(N = \{10^4,5 \times 10^4,10^5,5 \times
10^5,10^6,5 \times 10^6\}\), three different covariate sizes
\(\{10,25,50\}\), and three different
model sizes \(\{3,5,10\}\), the
functions were replicated \(100\)
times. When using the model-robust subsampling functions, the initial
subsample sizes \(r_0=\{100,250,500\}\)
were selected based on the covariate sizes, while the final subsample
size was fixed at \(r_f=2500\). Here,
the models included in the model set are selected based on their AIC
values, with a squared term derived from the main effects.
N_size<-c(1,5,10,50,100,500)*10000
N_size_labels<-c("10^4","5 x 10^4","10^5","5 x 10^5","10^6","5 x 10^6")
CS_size<-c(10,25,50)
NOM_size<-c(3,5,10)
N_and_CS_size <- c(t(outer(CS_size, N_size_labels,
function(cs, n) paste0("N = ",n,
" and \nNumber of Covariates ",cs))))This implementation was conducted on a high-performance computing system; however, the code for linear regression-related functions is shown below. Furthermore, it can be extended to logistic and Poisson regression using the relevant subsampling functions and model configurations.
# load the packages
library(NeEDS4BigData)
library(here)
library(biglm)
# indexes for N, covariate sizes and number of models
indexA <- as.numeric(Sys.getenv("indexA"))
indexB <- as.numeric(Sys.getenv("indexB"))
indexC <- as.numeric(Sys.getenv("indexC"))
# set N, covariate size, number of models and assign replicates
N_size<-c(1,5,10,50,100,500)*10000
Covariate_size<-c(10,25,50)
No_of_Models<-c(3,5,10)
Replicates<-100
# set the initial and final subsample sizes,
# with the distribution parameters to generate data
r0<-c(1,2.5,5)*100; rf<-2500;
Dist<-"Normal"; Dist_Par<-list(Mean=0,Variance=1,Error_Variance=0.5);
Family<-"linear"
# assign the indexes
N_idx<-indexA; Covariate_idx<-indexB; ModelSet_idx<-indexC
No_Of_Var<-Covariate_size[Covariate_idx]
N<-N_size[N_idx]
Model_Set<-No_of_Models[ModelSet_idx]
# generate the big data based on N and covariate size
Beta<-c(-1,rep(0.5,Covariate_size[Covariate_idx]))
Generated_Data<-GenGLMdata(Dist,Dist_Par,No_Of_Var,Beta,N,Family)
Full_Data<-Generated_Data$Complete_Data
# Find the models in the model set for model-robust subsampling
# based on AIC values
Full_Data<-cbind(Full_Data,Full_Data[,-c(1,2)]^2)
colnames(Full_Data)<-c("Y",paste0("X",0:No_Of_Var),paste0("X",1:No_Of_Var,"^2"))
Temp_Data<-Full_Data[sample(1:N,1000),]
AIC_Values<-NULL
for (i in 1:No_Of_Var) {
temp_data<-as.data.frame(Temp_Data[,c("Y",paste0("X",0:No_Of_Var),paste0("X",i,"^2"))])
model <- lm(Y~.-1, data = temp_data)
AIC_Values[i]<-AIC(model)
}
# Covariates in model set
Best_Indices <- order(AIC_Values)[1:Model_Set]
Model_Apriori<-rep(1/Model_Set,Model_Set)
All_Combinations<-lm_formula<-list();
for (NOM_idx in 1:Model_Set) {
All_Combinations[[NOM_idx]]<-c(paste0("X",0:No_Of_Var),
paste0("X",Best_Indices[NOM_idx],"^2"))
lm_formula[[NOM_idx]]<-as.formula(paste("Y ~",
paste(c(paste0("X",0:No_Of_Var),
paste0("X",Best_Indices[NOM_idx],"^2")),
collapse = " + ")))
}
cat("N size :",N_size[N_idx]," and Covariate size :",Covariate_size[Covariate_idx],
" with the model set ",No_of_Models[ModelSet_idx],"\n")
# benchmarking the stats::lm() function
lm<-sapply(1:Replicates,function(i){
start_T<-Sys.time()
for(NOM_idx in 1:length(lm_formula)){
suppressMessages(lm(lm_formula[[NOM_idx]],data=data.frame(Full_Data)))
}
return(difftime(Sys.time(),start_T,units = "secs"))
})
cat("Benchmarked lm() function.\n")
# benchmarking the biglm::biglm() function
biglm<-sapply(1:Replicates,function(i){
start_T<-Sys.time()
for (NOM_idx in 1:length(lm_formula)) {
suppressMessages(biglm(lm_formula[[NOM_idx]],data=data.frame(Full_Data)))
}
return(difftime(Sys.time(),start_T,units = "secs"))
})
cat("Benchmarked biglm() function.\n")
# benchmarking the NeEDS4BigData::modelRobustLinSub() function
modelRobustLinSub<-sapply(1:Replicates,function(i){
start_T<-Sys.time()
suppressMessages(modelRobustLinSub(r0[Covariate_idx],rf,
Y=as.matrix(Full_Data[,1]),
X=as.matrix(Full_Data[,-1]),
N=nrow(Full_Data),
Apriori_probs=Model_Apriori,
All_Combinations = All_Combinations,
All_Covariates = colnames(Full_Data[,-1])))
return(difftime(Sys.time(),start_T,units = "secs"))
})
cat("Benchmarked modelRobustLinSub() function.")
Plot_Data<-cbind.data.frame("N size"=N_size[N_idx],
"Covariate size"=Covariate_size[Covariate_idx],
"No of Models"= No_of_Models[ModelSet_idx],
"lm()"=lm,"biglm()"=biglm,
"modelRobustLinSub()"=modelRobustLinSub)
save(Plot_Data,
file=here("Results",paste0("Output_NS_",N_idx,"_CS_",Covariate_idx,
"_MS_",ModelSet_idx,".RData")))Linear regression
For linear regression, the modelRobustLinSub() function
from the NeEDS4BigData package was compared against lm()
and biglm().
Functions_FCT<-c("lm()","biglm()","modelRobustLinSub()")
Functions_Colors<-c("cornsilk4","black","#50FF50")
Final_Linear_Regression %>%
mutate(Functions=factor(Functions,levels = Functions_FCT,labels = Functions_FCT),
`N size`=factor(`N size`,levels = N_size,labels = N_size_labels),
`N and Covariate size`=paste0("N = ",`N size`,
" and \nNumber of Covariates ",
`Covariate size`)) %>%
mutate(`N and Covariate size`=factor(`N and Covariate size`,
levels = N_and_CS_size,
labels = N_and_CS_size)) %>%
select(`N and Covariate size`,`No of Models`,Functions,Time) %>%
group_by(`N and Covariate size`,`No of Models`,Functions) %>%
summarise(Mean=mean(Time),min=quantile(Time,0.05),max=quantile(Time,0.95),
.groups = "drop") %>%
ggplot(.,aes(x=factor(`No of Models`),y=Mean,color=Functions,group=Functions))+
geom_point(position = position_dodge(width = 0.5))+
geom_line(position = position_dodge(width = 0.5))+
geom_errorbar(aes(ymin=min,ymax=max),position = position_dodge(width = 0.5))+
facet_wrap(.~factor(`N and Covariate size`),scales = "free",ncol=length(N_size))+
xlab("Number of Models")+ylab("Time in Seconds")+
scale_color_manual(values = Functions_Colors)+
theme_bw()+Theme_special()+ggtitle("Linear Regression")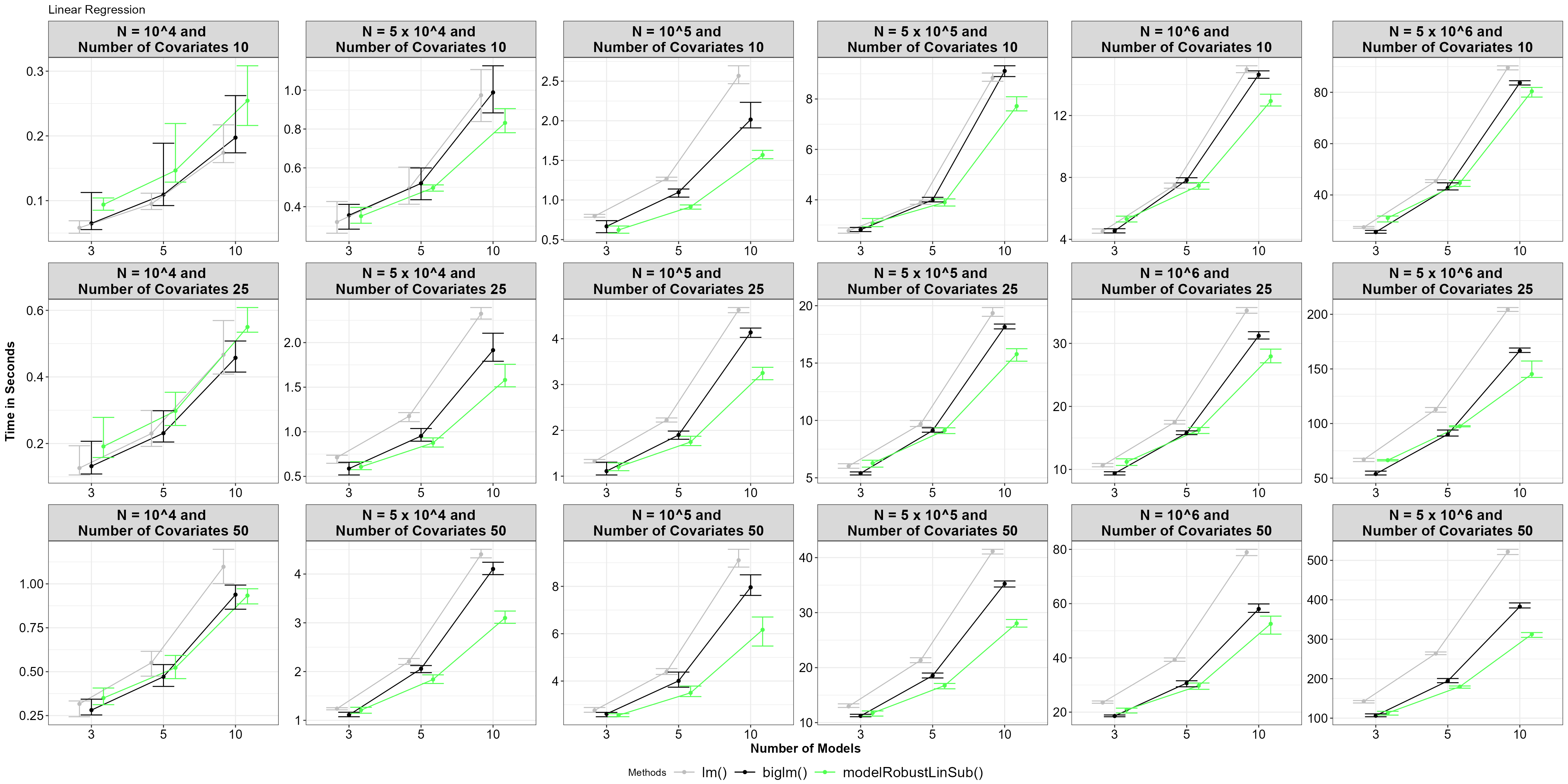
Average time for functions, with 5% and 95% percentile intervals under model robust linear regression.
In general, our subsampling functions perform faster as the size of
the big data, the number of covariates, and the number of models
increase. Even when a solution for linear regression is available in an
analytical form, the subsampling functions perform better than or as
well as biglm().
Logistic regression
For logistic regression, the modelRobustLogSub()
function was compared against glm() and
bigglm().
Functions_FCT<-c("glm()","bigglm()","modelRobustLogSub()")
Functions_Colors<-c("cornsilk4","black","#50FF50")
Final_Logistic_Regression %>%
mutate(Functions=factor(Functions,levels = Functions_FCT,labels = Functions_FCT),
`N size`=factor(`N size`,levels = N_size,labels = N_size_labels),
`N and Covariate size`=paste0("N = ",`N size`,
" and \nNumber of Covariates ",
`Covariate size`)) %>%
mutate(`N and Covariate size`=factor(`N and Covariate size`,
levels = N_and_CS_size,
labels = N_and_CS_size)) %>%
select(`N and Covariate size`,`No of Models`,Functions,Time) %>%
group_by(`N and Covariate size`,`No of Models`,Functions) %>%
summarise(Mean=mean(Time),min=quantile(Time,0.05),max=quantile(Time,0.95),
.groups = "drop") %>%
ggplot(.,aes(x=factor(`No of Models`),y=Mean,color=Functions,group=Functions))+
geom_point(position = position_dodge(width = 0.5))+
geom_line(position = position_dodge(width = 0.5))+
geom_errorbar(aes(ymin=min,ymax=max),position = position_dodge(width = 0.5))+
facet_wrap(.~factor(`N and Covariate size`),scales = "free",ncol=length(N_size))+
xlab("Number of Models")+ylab("Time in Seconds")+
scale_color_manual(values = Functions_Colors)+
theme_bw()+Theme_special()+ggtitle("Logistic Regression")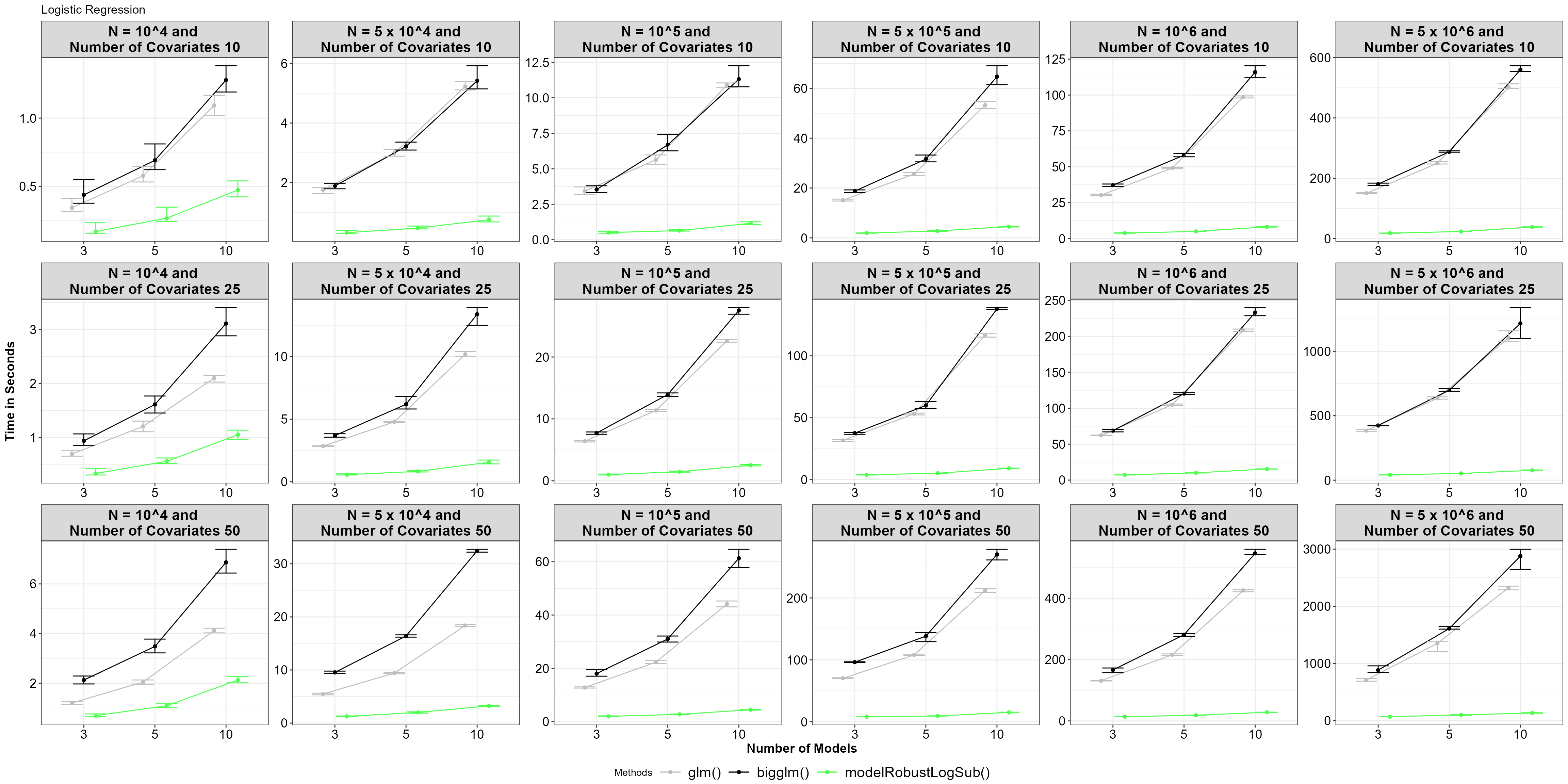
Average time for functions, with 5% and 95% percentile intervals under model robust logistic regression.
It seems there is a significant difference between using
glm() and bigglm(), with the model-robust
subsampling function performing faster. This performance gap increases
as the size of the big data, the number of covariates, and the number of
models grow.
Poisson Regression
For Poisson regression, the function modelRobustPoiSub()
was compared against glm() and bigglm().
Functions_FCT<-c("glm()","bigglm()","modelRobustPoiSub()")
Functions_Colors<-c("cornsilk4","black","#50FF50")
Final_Poisson_Regression %>%
mutate(Functions=factor(Functions,levels = Functions_FCT,labels = Functions_FCT),
`N size`=factor(`N size`,levels = N_size,labels = N_size_labels),
`N and Covariate size`=paste0("N = ",`N size`,
" and \nNumber of Covariates ",
`Covariate size`)) %>%
mutate(`N and Covariate size`=factor(`N and Covariate size`,
levels = N_and_CS_size,
labels = N_and_CS_size)) %>%
select(`N and Covariate size`,`No of Models`,Functions,Time) %>%
group_by(`N and Covariate size`,`No of Models`,Functions) %>%
summarise(Mean=mean(Time),min=quantile(Time,0.05),max=quantile(Time,0.95),
.groups = "drop") %>%
ggplot(.,aes(x=factor(`No of Models`),y=Mean,color=Functions,group=Functions))+
geom_point(position = position_dodge(width = 0.5))+
geom_line(position = position_dodge(width = 0.5))+
geom_errorbar(aes(ymin=min,ymax=max),position = position_dodge(width = 0.5))+
facet_wrap(.~factor(`N and Covariate size`),scales = "free",ncol=length(N_size))+
xlab("Number of Models")+ylab("Time in Seconds")+
scale_color_manual(values = Functions_Colors)+
theme_bw()+Theme_special()+ggtitle("Poisson Regression")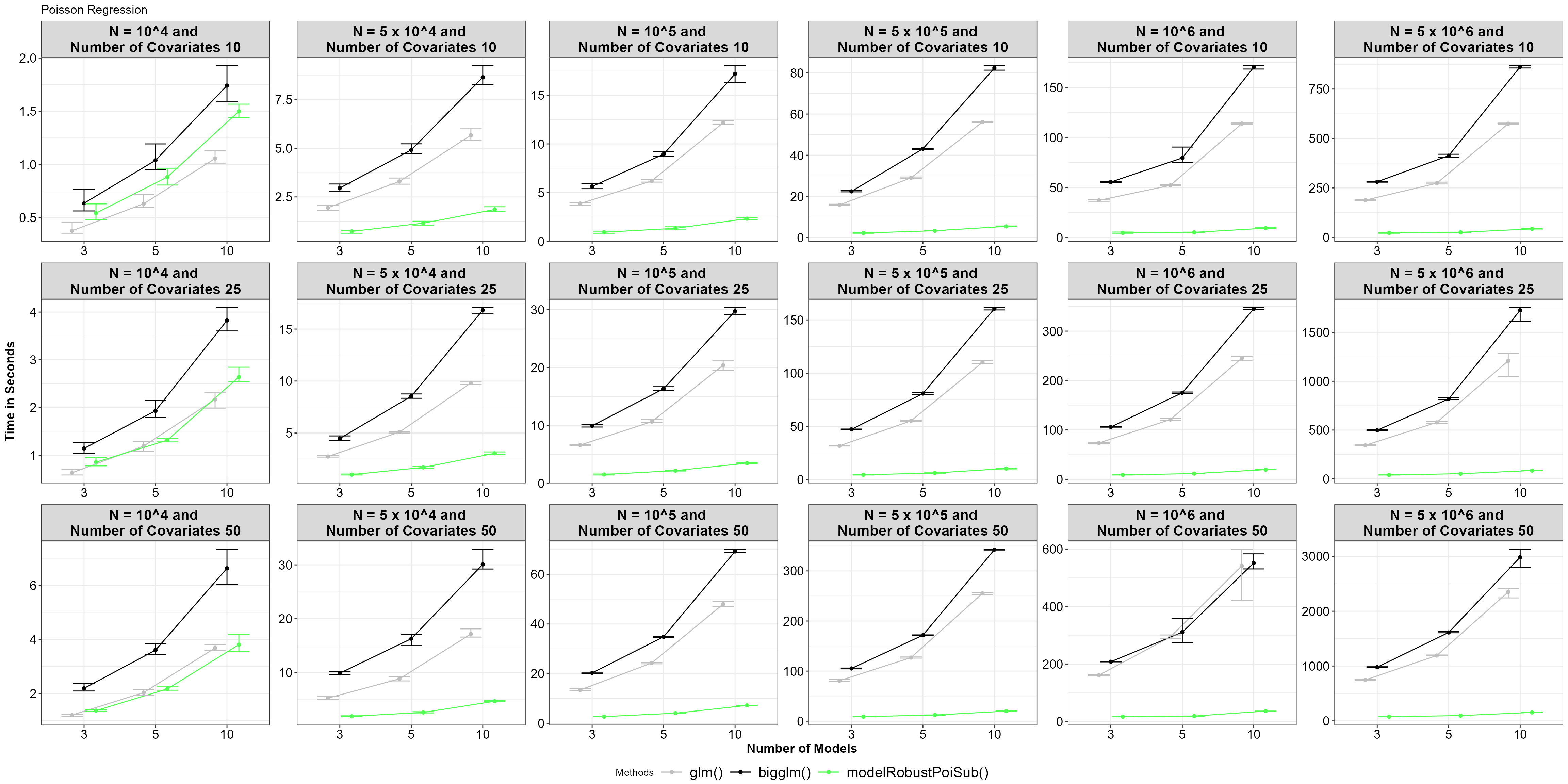
Average time for functions, with 5% and 95% percentile intervals under model robust Poisson regression.
Similar to logistic regression, the model-robust subsampling function
performs faster than the glm() and bigglm()
functions.
In summary, the model-robust subsampling functions available in this R package perform best under high-dimensional data.