These functions provide the ability for generating probability density values, cumulative probability density values and moments about zero values for the Uniform Distribution bounded between [0,1].
Value
The output of dUNI gives a list format consisting
pdf probability density values in vector form.
mean mean of unit bounded uniform distribution.
var variance of unit bounded uniform distribution.
Details
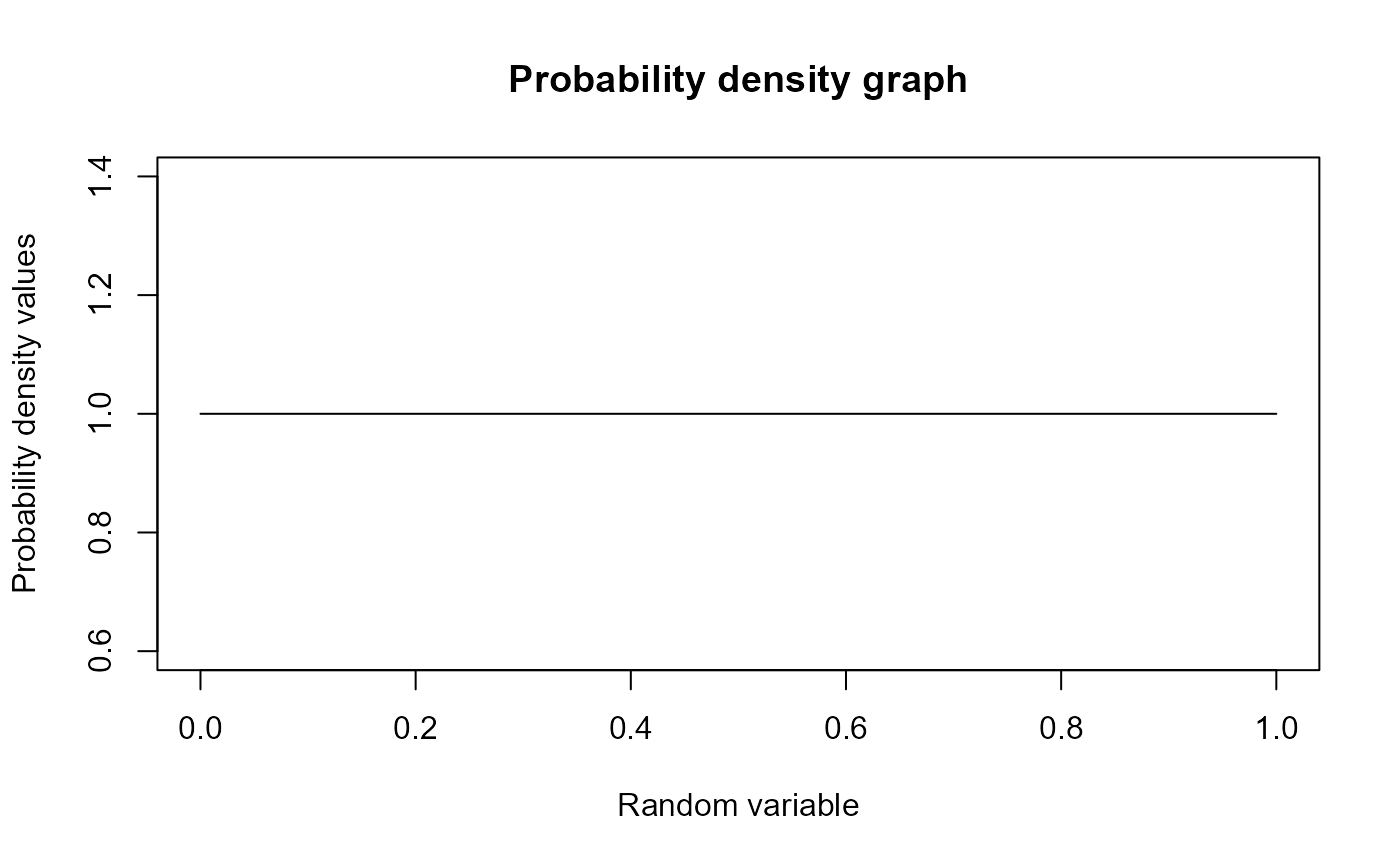
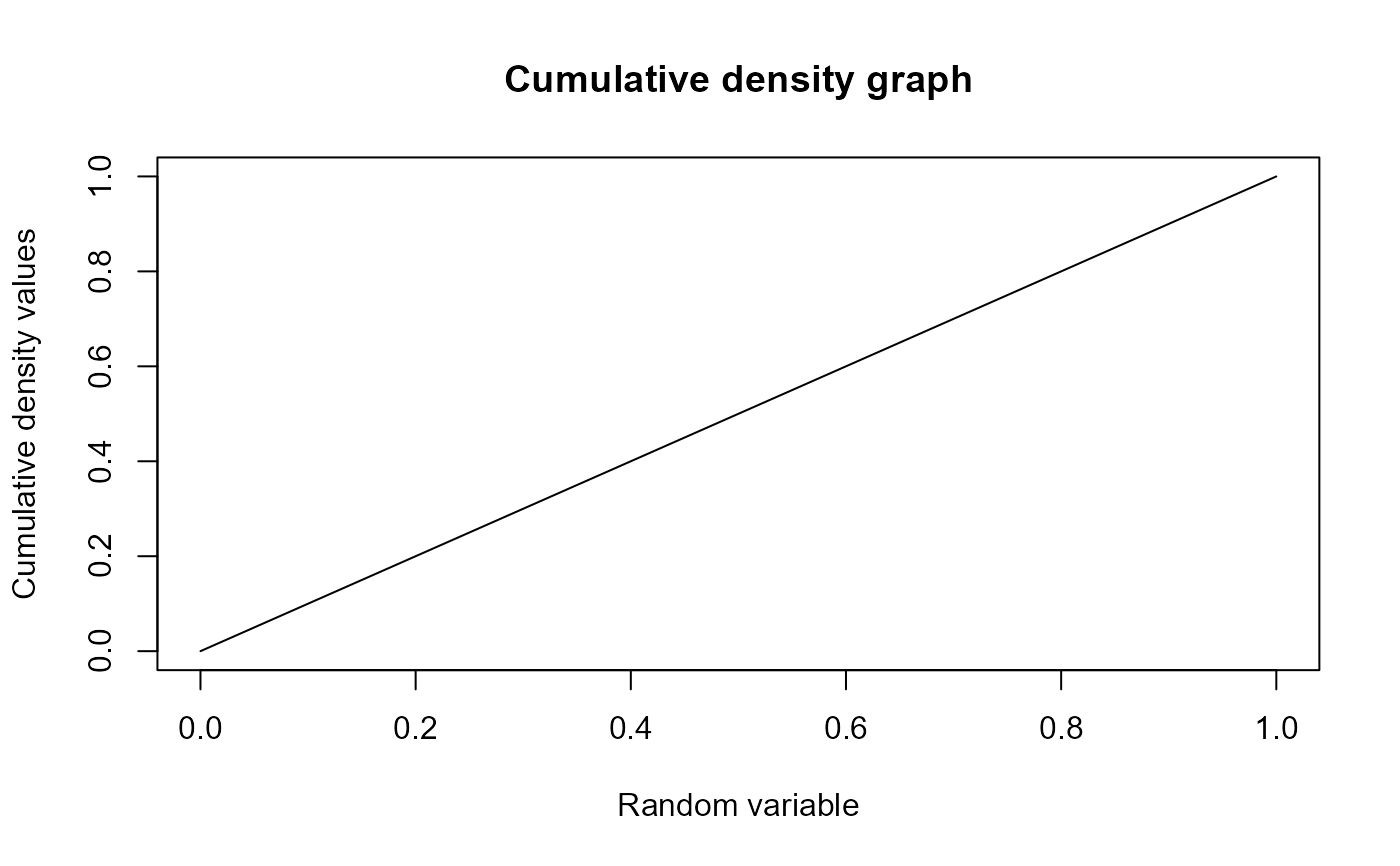
Setting \(a=0\) and \(b=1\) in the Uniform Distribution a unit bounded Uniform Distribution can be obtained. The probability density function and cumulative density function of a unit bounded Uniform Distribution with random variable P are given by
$$g_{P}(p) = 1$$ \(0 \le p \le 1\) $$G_{P}(p) = p$$ \(0 \le p \le 1\)
The mean and the variance are denoted as $$E[P]= \frac{1}{a+b}= 0.5$$ $$var[P]= \frac{(b-a)^2}{12}= 0.0833$$
Moments about zero is denoted as $$E[P^r]= \frac{e^{rb}-e^{ra}}{r(b-a)}= \frac{e^r-1}{r} $$ \(r = 1,2,3,...\)
NOTE : If input parameters are not in given domain conditions necessary error messages will be provided to go further.
References
Horsnell G (1957). “Economical acceptance sampling schemes.” Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series A (General), 120(2), 148--201. Johnson NL, Kotz S, Balakrishnan N (1995). Continuous univariate distributions, volume 2, volume 289. John wiley and sons.
Examples
#plotting the random variables and probability values
plot(seq(0,1,by=0.01),dUNI(seq(0,1,by=0.01))$pdf,type = "l",main="Probability density graph",
xlab="Random variable",ylab="Probability density values")
 dUNI(seq(0,1,by=0.05))$pdf #extract the pdf values
#> [1] 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
dUNI(seq(0,1,by=0.01))$mean #extract the mean
#> [1] 0.5
dUNI(seq(0,1,by=0.01))$var #extract the variance
#> [1] 0.08333333
#plotting the random variables and cumulative probability values
plot(seq(0,1,by=0.01),pUNI(seq(0,1,by=0.01)),type = "l",main="Cumulative density graph",
xlab="Random variable",ylab="Cumulative density values")
dUNI(seq(0,1,by=0.05))$pdf #extract the pdf values
#> [1] 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
dUNI(seq(0,1,by=0.01))$mean #extract the mean
#> [1] 0.5
dUNI(seq(0,1,by=0.01))$var #extract the variance
#> [1] 0.08333333
#plotting the random variables and cumulative probability values
plot(seq(0,1,by=0.01),pUNI(seq(0,1,by=0.01)),type = "l",main="Cumulative density graph",
xlab="Random variable",ylab="Cumulative density values")
 pUNI(seq(0,1,by=0.05)) #acquiring the cumulative probability values
#> [1] 0.00 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.30 0.35 0.40 0.45 0.50 0.55 0.60 0.65 0.70
#> [16] 0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00
mazUNI(c(1,2,3)) #acquiring the moment about zero values
#> [1] 0.5000000 0.3333333 0.2500000
#only the integer value of moments is taken here because moments cannot be decimal
mazUNI(1.9)
#> [1] 0.5
pUNI(seq(0,1,by=0.05)) #acquiring the cumulative probability values
#> [1] 0.00 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.30 0.35 0.40 0.45 0.50 0.55 0.60 0.65 0.70
#> [16] 0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 1.00
mazUNI(c(1,2,3)) #acquiring the moment about zero values
#> [1] 0.5000000 0.3333333 0.2500000
#only the integer value of moments is taken here because moments cannot be decimal
mazUNI(1.9)
#> [1] 0.5