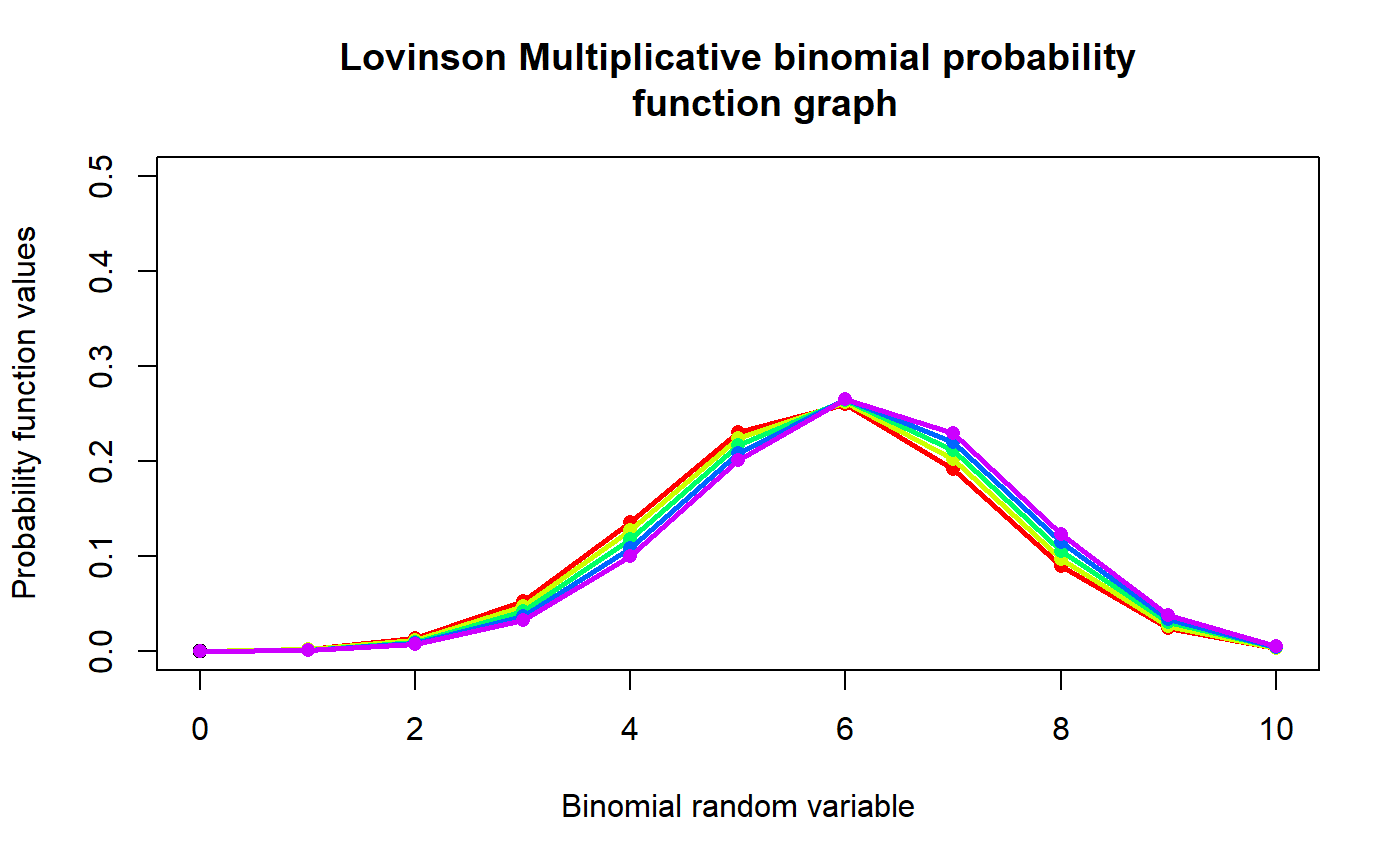
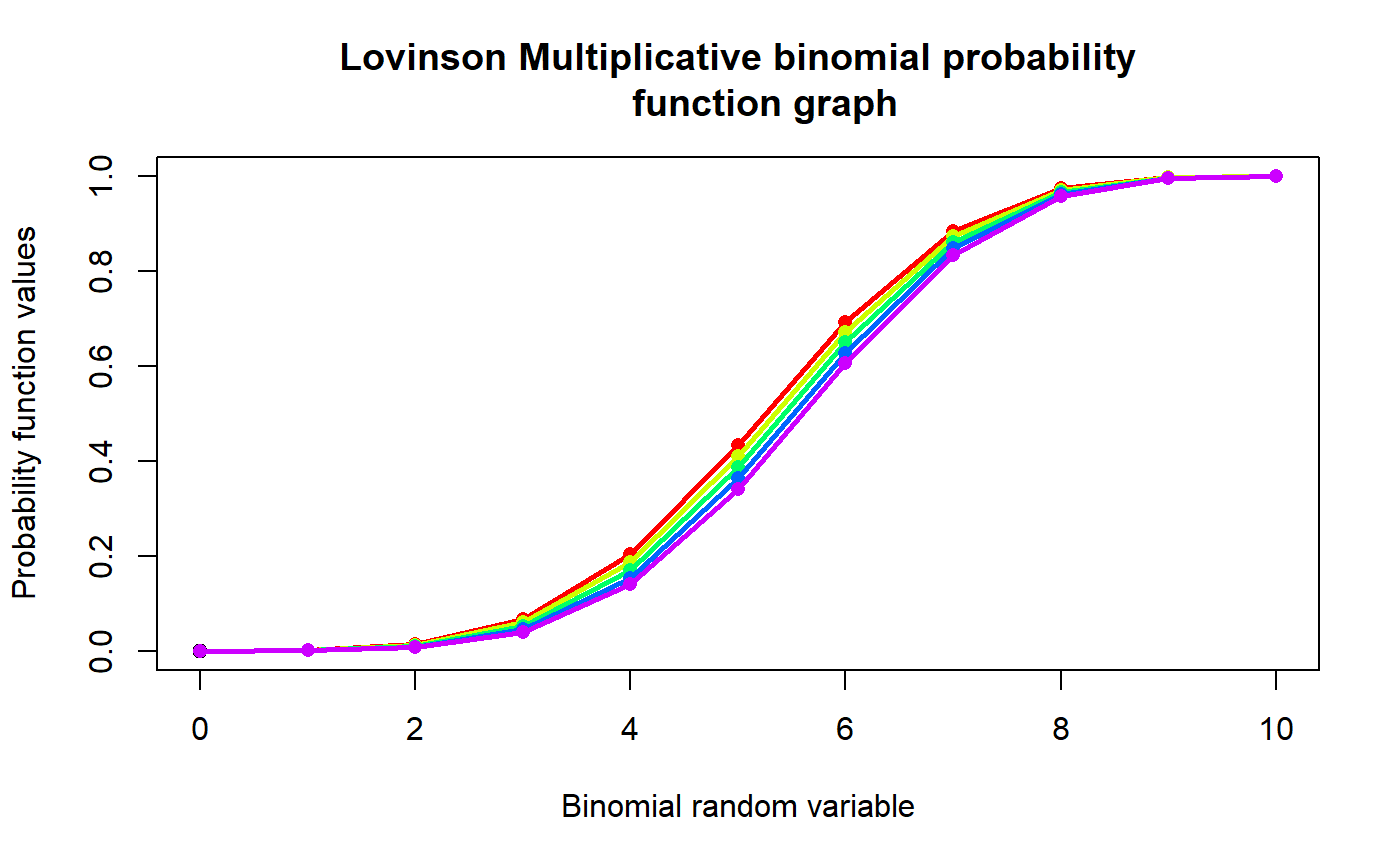
These functions provide the ability for generating probability function values and cumulative probability function values for the Lovinson Multiplicative Binomial Distribution.
pLMBin(x,n,p,phi)
Arguments
| x | vector of binomial random variables. |
|---|---|
| n | single value for no of binomial trials. |
| p | single value for probability of success. |
| phi | single value for phi. |
Value
The output of pLMBin gives cumulative probability values in vector form.
Details
The probability function and cumulative function can be constructed and are denoted below
The cumulative probability function is the summation of probability function values.
$$P_{LMBin}(x)= {n \choose x} p^x (1-p)^{n-x} \frac{(phi^{x(n-x)}}{f(p,phi,n)} $$
here \(f(p,phi,n)\) is $$f(p,phi,n)= \sum_{k=0}^{n} {n \choose k} p^k (1-p)^{n-k} (phi^{k(n-k)} )$$
$$x = 0,1,2,3,...n$$ $$n = 1,2,3,...$$ $$k = 0,1,2,...,n$$ $$0 < p < 1$$ $$0 < phi $$
NOTE : If input parameters are not in given domain conditions necessary error messages will be provided to go further.
References
Elamir, E.A., 2013. Multiplicative-Binomial Distribution: Some Results on Characterization, Inference and Random Data Generation. Journal of Statistical Theory and Applications, 12(1), pp.92-105.
Examples
#plotting the random variables and probability values col <- rainbow(5) a <- c(0.58,0.59,0.6,0.61,0.62) b <- c(0.022,0.023,0.024,0.025,0.026) plot(0,0,main="Lovinson Multiplicative binomial probability function graph",xlab="Binomial random variable", ylab="Probability function values",xlim = c(0,10),ylim = c(0,0.5))for (i in 1:5) { lines(0:10,dLMBin(0:10,10,a[i],1+b[i])$pdf,col = col[i],lwd=2.85) points(0:10,dLMBin(0:10,10,a[i],1+b[i])$pdf,col = col[i],pch=16) }#> [1] 6.364309e-29 8.964365e-19 5.657070e-11 2.106255e-05 5.123785e-02 #> [6] 8.509524e-01 9.771209e-02 7.659947e-05 3.923411e-10 1.185630e-17 #> [11] 1.605234e-27#> [1] 5.046585#> [1] 0.1471704#plotting random variables and cumulative probability values col <- rainbow(5) a <- c(0.58,0.59,0.6,0.61,0.62) b <- c(0.022,0.023,0.024,0.025,0.026) plot(0,0,main="Lovinson Multiplicative binomial probability function graph",xlab="Binomial random variable", ylab="Probability function values",xlim = c(0,10),ylim = c(0,1))for (i in 1:5) { lines(0:10,pLMBin(0:10,10,a[i],1+b[i]),col = col[i],lwd=2.85) points(0:10,pLMBin(0:10,10,a[i],1+b[i]),col = col[i],pch=16) }pLMBin(0:10,10,.58,10.022) #acquiring the cumulative probability values#> [1] 6.364309e-29 8.964365e-19 5.657070e-11 2.106261e-05 5.125891e-02 #> [6] 9.022113e-01 9.999234e-01 1.000000e+00 1.000000e+00 1.000000e+00 #> [11] 1.000000e+00